Machinery
CAISA has the following machinery to carry out their work. The machinery necessary to complete the different process phases is explained in detail as follows, and each of the machines' main characteristics are shown.
- Cylinder machine
- Bending machine
- Lathe
- Tejero blender
- Geka 55 puncher
- Machine plasma
- Welding equipment
-
CYLINDER MACHINE:
 Prebending of metallic sheet at 22mm - Bending metallic sheet at 15mm
Prebending of metallic sheet at 22mm - Bending metallic sheet at 15mmThe metallic sheet turning is a procedure to curve or wind the metallic sheet by means of mechanical or hydraulic force until reaching the required radius, with no need to subject the material to higher temperatures.
The upper roller above the two lower rollers makes it use hydraulic oil in the cylinder to act on the piston and raise vertically.The controller's last gear handles the lower roller's gears so it turns, which provides torque to the plate. This three-roller hydraulic machine's main structure includes:
- Upper roller
- Lower roller
- Main transmission device
- Including and chassis device
The metallic sheet may be bent or wrapped with no difficulty along almost the entire length (or width) of the metallic sheet, but a few centimetres from the edges toward the centre of the sheet cannot be completely "bent into a cylinder." This limitation is known as "Pre-bending", or edge bending. In other words, folding made with the force of the side roller.
Pre-bending comes about due to the distance between the three 3 mooring rollers, and they are the metallic sheet's centimetres measured from the mooring point between the rollers and the support point on the side roller, and this must take place on the two edges of the metallic sheet, or before and after its entire length is passed and its edges enter into contact with the rollers.
In this position, the edges cannot be bent into a cylinder and must be bent solely by the force from the lateral roller's movement, which is elevated by pressing and bending this edge of section of the metallic sheet, which normally reaches a radius lower than the one sought. At times, the machine operator leaves them without processing them, leaving them straight to later cut them and dispose of them; on other occasions, they curve them with a bending machine in progressive fashion by sections. Like the side roller when it rises, bending the edge of the metallic sheet, it carries out a "pressing" and not a cylinder-making operation, with rated capacity for the machine being lower.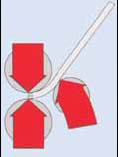
For decades, this method has been used to bend the metallic sheets that provide and infinity of elements in the construction, of which are noteworthy: silos, petrol and water tanks, boilers, heat exchangers, and other equipment for civil works.
-
BENDING MACHINE:
 240Tn of bending sheet metal up to 20mm (1m)
240Tn of bending sheet metal up to 20mm (1m)The benders are press-type machines used for cold work on sheet metal. Folding (bending) is the process of putting a piece of sheet metal between a bunch and a matrix and subjecting said sheet to force by means of the machine, so that the sheet bends with a constant radius. With bending, we contribute rigidity to the part and we attain tri-dimensional geometry, avoiding welding.
The thickness of the sheets to be bent tends to be 0.5 to 20 mm, and it ranges in length from a few centimetres to several metres.
Basically, two types of work are distinguished for this process:
-
Air bending:
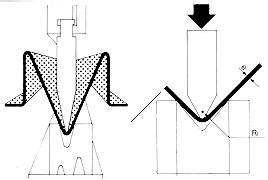 This type of bending is characterised because the punch does not bring the sheet to the bottom of the matrix and leaves a bending angle. It is generally used for sheets with thicknesses greater than 2 mm.
This type of bending is characterised because the punch does not bring the sheet to the bottom of the matrix and leaves a bending angle. It is generally used for sheets with thicknesses greater than 2 mm. -
Bottom folding:
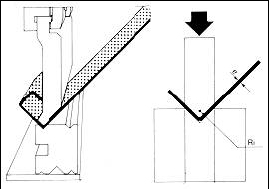 With this, the punch brings the sheet to the bottom of the matrix. It is used for sheets with thicknesses less than 2 mm. The work method consists of:
With this, the punch brings the sheet to the bottom of the matrix. It is used for sheets with thicknesses less than 2 mm. The work method consists of:
- Placing the part, supported rear stops, in the bending area.
- Activating the control system (pedal, bar, button...).
- Holding the part, accompanying it in its upward bending movement.
- Extracting the bent part.
In addition to the aforementioned basic work, these machines may also be used for adjustment and punching work.
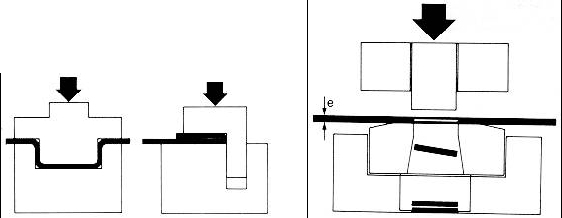
Although normally there are stops and consoles to ease work for the operator when placing the part, it is also true that the operator must generally hold the sheet during bending to keep it from falling. According to the sheet metal's dimensions, the operation may require the presence of two operators.
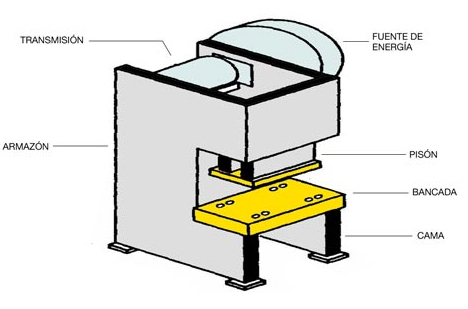
The main elements making up a Bending Machine as observed in the figure are:
- The Frame is the machine's pysical construction.
- The Bench or transversal plate is a welded part upon which the machine is supported. It has the work table on its upper part, upon which the sheet metal to be bent is supported, and where the matrices and centring and positioning systems are housed.
- The Ram, Tamp or upper table is generally the mobile part of the machine where punches are housed for bending. Normally, the ram carries out operation by means of downward movement.
- The Bed or lower table is a vertical metallic plate, generally fixed in position, located on the same plane as the ram, upon which the bending matrix is supported (on occasions, this table can be mobile, and when this occurs, the ram is fixed).
- The Transmission is a mechanism made up of different gears and pulleys in charge of transmitting power by a Power Source within the machine, to make the Tamp move.
- The Controls to activate the machine may be pedals, bars or push buttons; generally, there is a selector to choose the activation system if several of them co-exist.
The main tools and accessories used by the bending machine are:
- Limit stops.
- Rear material positioning stops.
- Retractable stops and consoles.
- Safety devices.
- Placement limiters.
- Operation selector.
In hydraulic bending machines, the operation is carried out in two phases:
- Approaching phase, with rapid closure of the ram.
- Work phase corresponding to bending itself at slow speed.
-
-
LATHE for small mechanisations

Machine that mechanises geometric spin-shaped parts. This machine operates by making the part to be mechanised spin (held at the head or the centring points), while one or several cutting tools are pushed in a regulated forward movement against the part's surface, shaving off according to the appropriate mechanisation technological conditions.
The cutting tool is assembled on a cart that is moved on guides or rails parallel to the rotation axis of the part being lathed, called axis Z< there is another cart on this one that moves according to axis X, in a direction radial to the part being lathed, and there may be a third cart called a chariot that may be tilted, to make cones, where the tool/carrier turret is supported. When the main cart moves the tool along the rotation axis, the part takes on a cylinder shape, and when the transversal cart moves in perpendicular fashion to the part's symmetrical axis, the operation called "facing" is carried out.
-
TEJERO BENDER
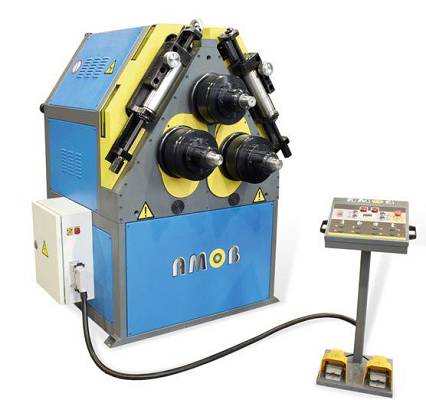

- Profile material bender model L-80CN
- Hydraulic clamping
- Axes with 90 diameter, the three motorised
- 7.5Hp to 380V Motor
- Digital lower roller positioning
- Bending capacity in T=80x8
- UPN=120x55
- TUBE with 90 x 3.5 diameter
- 132x132 strip, 55 Diameter, 50 squared
- Peso con accesorios 2,400kg
-
GEKA 55 PUNCHER

- Technically sixed bench
- Cylinder with supplementary guide
- Rod with anti-turn system, strong and precise
- Progressive puncher centring
- Rapid punch change
- Safety protections
- Great free space for assembling special equipment
- Excellent work speed
- Large variety of optional equipment, stamdard and special, for carrying out a broad range of work
- Range of punches from 50Tn to 220Tn with necks between 130mm. and 800mm
- Punch power 550KN
- Maximum capacity diameter 40 x 10mm
- Neck: 750mm
-
PLASMA MACHINE
Manual plasma cutting equipment is currently an indispensable tool for industry in general. They are highly useful for manufacturing and maintenance tasks for cutting metals, stainless steel, carbon steel and aluminium, in addition to others.

One of its characteristics is the portability of the equipment, which, due to its low weight, makes it easy to use in one's own facilities and on-site. On the other hand, most of these pieces of equipment also allow for placement of a torch for mechanised cuts. In other words, they may be installed on automatically progressing devices such as pantographs, forward-moving carts, pipe-cutting machines, robots, etc.
The arc-cutting process is a process where an open arc, similar to TIG welding, may be contracted by passing it through a small nozzle or orifice, from the electrode to the work piece. The gas used is typically air and is combined with electrical current to create a high-temperature plasma arc. When put into contact with a material that conducts electricity, the arc passes through the metal, melting a thin area. The strength of the arc pushes the melted metal through the work piece and cuts the material.
It is important to note the machine's work cycle as a number of minutes within a period of 10, wherein the welding machine operates at rated capacity. For example, a 300 ampere machine at 60% of the work cycle could operate at 300 amperes for 6 minutes, and would then have to cool down by means of its fan for 4 minutes.
Plasma cutting has several advantages in comparison with other cutting processes. Although there are other more common cutting methods, this plasma process:
- Cuts more quickly.
- Does not require a pre-heating cycle, which saves time and is more convenient.
- Makes a more precise indentation width (width of cut), excellent when precision is important.
- It has a smaller area affected by heat, which prevents the area around the cut from twisting or damaging paint.
Additionally, other processes cannot cut stainless steel or aluminium, while the plasma process can cut ANY type of metal that conducts electricity, including tin, copper, titanium and galvanised metals. Plasma cutting is fast and clean and leaves a straight line. It is also a less costly and more convenient cutting method in comparison with other processes, since compressed air coming from portable compressors or the shop is available in most applications.
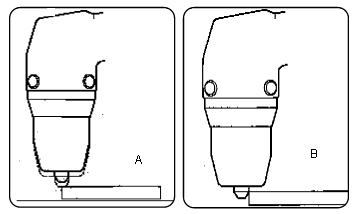
The output current needed by a plasma cutting machine fundamentally depends on the width and type of material that needs to be cut. Cutting speed makes a significant difference in production time and the operator's comfort. When beginning cutting, it should be done as shown in figure A, avoiding doing so as shown in figure B, keeping the torch vertical throughout the process.
Once completed and after having released the button, air will continue to exit through the torch for a few seconds to allow the torch to cool. It is not advised to turn the apparatus off before this time is completed.
The electrode must be replaced when it has a cavity on its rear part of approximately 1 mm. In the same fashion, the nozzle should be replaced when the orifice is no longer regular and cutting capacity has decreased.
For proper operation, you must always ensure that the arc completely penetrates the part to be cut and that it is never inclined in a forward direction at a degree greater than 10-15º. When the arc does not penetrate welded metal slag, the nozzle is obstructed. If the air contains a notable amount of humidity and oil, it is advised to use a drying filter to avoid excess oxidation and wear on consumption parts, damage to the torch and a reduction incutting speed and quality.
As an example, the following cutting table shows values for different materials.
MATERIAL THICKNESS CURRENT MAXIMUM CUTTING SPEED (pulg) (mm) (amps) (ppm) (mm/min) CARBON STEEL 18 calibre 1,3 30 3.94 10007 10 calibre 3,4 30 87 2210 2/6 4,8 30 52 1321 1/4 6,4 30 33 838 2/6 9,5 30 15 381 ALUMINIUM 18 calibre 1,3 30 3.99 10135 10 calibre 3,4 30 78 1981 1/4 6,4 30 26 660 2/6 9,5 30 11 279 STAINLESS STEEL 18 calibre 1,3 30 2.21 5613 10 calibre 3,4 30 55 1397 1/4 6,4 30 24 610 2/6 9,5 30 11 279 Plasma cutting produces smoke and gases that may be damaging to health. Good ventilation and appropriate attire are required to avoid these problems.
-
WELDING EQUIPMENT:
Equipment CAISA currently has available is:
-
TIG welding
The machine welds with tungsten by means of an input bar using argon gas to prevent welding rust, at the same time that the machine carries a transformer with a rectifier bridge with a continuous circuit. -
Welding with COATED ELECTRODE
This is characterised by the creation and maintenance of an electric arc between the metallic rod (electrode) and the part to be welded. The coated electrode is made up of a metallic rod covered with non-metallic substances, according to the characteristics required for use. The coating used at CAISA is basic and rutile. To perform electric arc welding, a difference in potential is induced between the electrode and the part to be welded, which ionises the air between them and becomes a conductor, so the circuit is closed. The heat from the arc partially welds the base material and melts the filler material, which is deposited and creates the welding bead. Welding by electric arc is commonly used due to how easy it is to transport the equipment. -
MIG-MAG welding
This is an arc welding process under a protective gas with a consumable electrode, wherein the arc is produced by means of an electrode formed by a continuous thread and the parts to be joined, being protected from the surrounding atmosphere by an inert gas (MIG welding) or an active gas (MAG welding). This is a versatile process that can deposit weld metal at a high speed in all positions. It is highly used for small and medium thicknesses for steel structures and aluminium alloys, especially where much manual work is required.
-

